China’s Tax Reforms Tackle the Wealth Gap
The gap between the rich and poor in China is getting disturbingly wide with the GINI coefficient, a measure of income inequality, reaching 0.474 (and even higher by some accounts), well above the 0.4 level that is considered the threshold for breeding social discontent. To address the yawning gap, the State Council this month came out with a set of guidelines aimed at heavier taxes for SOE companies, property speculators, and the rich, among other measures.
Jointly announced by the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Finance, and the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, the reform plan also called for the doubling of 2010 personal incomes by 2020, setting a minimum wage in certain industries, narrowing wage gaps among SOEs, and 20% of housing stocks being low income by 2015.
One of the biggest impacts will felt by SOEs and listed Chinese companies. SOEs will be required to transfer 5% more of their profits to the government by the end of the 12th 5-Year Plan period (2015) and listed companies will have to raise their dividend payments to individual investors. SOEs have long enjoyed preferential policies that provided an uneven playing field on which they earned inordinate profits. Increased SOE taxation would go far in supporting pension funds, the national health insurance system, and other aspects of the social safety net.
“For state-owned companies in some industries with overly high income, we will strictly implement the two-tier controls on firms’ total salary and wage level to gradually reduce the salary gap between different industries”, stated the announcement. The government will also take a whip to state monopolies, bringing in stricter supervision to prevent improper access to public resources at little or no cost.
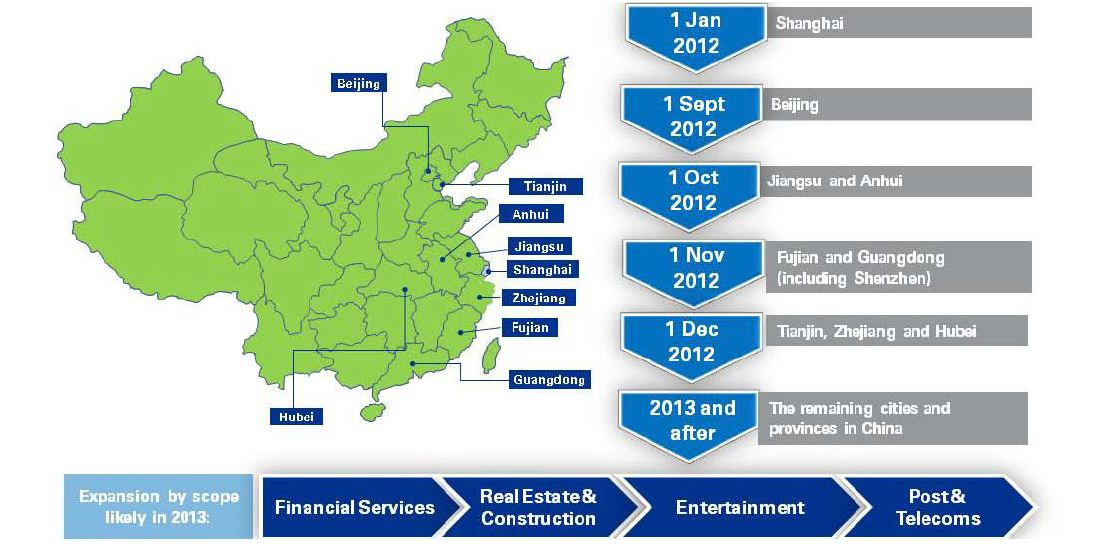
Taxes payable by SMEs that comprise 95% of all businesses in China will be reduced with the expansion of value-added tax (VAT) pilot projects that started in Shanghai since January 2012, introducing new VAT rates in transportation and modern services. During the second half of 2012, the program was expanded throughout the country and in 2013, VAT reforms will be extended to other industries such as financial services, insurance, real estate and construction, and others. If all goes well, all forms of business taxes will be amalgamated into VATs by as early as 2015.
The current tax system for individual income earners is full of loopholes through which the rich easily dodge auditors and previous plans for the introduction of a property tax have encountered much opposition. The new State Council guidelines introduces stricter rules for income and property disclosures by government officials, additional taxes on luxury products and leisure activities, augmentation of resource taxes, and the gradual implementation of a property tax pilot scheme on high-value houses.
The government will also study the introduction of an inheritance tax “at an appropriate date”. For foreign ex-pats, the exemption on dividends paid by foreign-funded enterprises from personal income taxes will also be withdrawn. Currently, average wage-earners contribute more than 60% of all personal income taxes in China.
In its China Rebalanced report, Fitch Ratings concludes that the government’s plan is likely to increase real wages and accelerate China’s economic rebalancing from investment-led to consumption led growth. “We would expect China’s rebalancing away from the existing unsustainable investment-led growth to lead to companies making more higher value-added goods and the development of service-based industries. We think it is likely that real wages will continue increasing even after investment as a share of GDP starts to fall, similar to Korea’s experience in the 1990s”, wrote the authors.
China to Build Titanic II
A Chinese shipyard will build an 885-foot-long ship to be named Titanic II — a replica of the liner that sank in 1912, a spokesman said.
The project, which will take the state-owned CSC Jinling Shipyard Co Ltd in Nanjing, Jiangsu province, three years to complete, is financed by Australian billionaire Clive Palmer, China Daily reported.
The 173-foot tall Titanic II will make its maiden voyage from England to the United States in 2016 with 900 crew members and 2,400 passengers, officials said.
“The world’s leading shipyards and ship-design companies, including Finland’s Deltamarin, have been invited to join the construction work of Titanic II,” said Li Wenbao, spokesman for Jinling. “The liner will be equipped with advanced technologies, including the latest life-saving and communications systems, to meet the requirements of modern navigation.”
Li said the shipyard has a contract with Blue Star Line, a wholly owned subsidiary of a mineralogy company owned by Palmer.
The original Titanic sank off Newfoundland after hitting an iceberg April 15, 2012, on its maiden voyage, killing 1,523 people.
– UPI
Low Level of Trust Among Chinese People
Trust among people in China dipped to a record low with less than half of respondents to a recent survey feeling that “most people can be trusted” while only about 30 per cent trusted strangers.
The Blue Book of Social Mentality, the latest annual report on the social mentality of China, analysed respondents’ trust toward different people and organisations and drew a conclusion that trust in society is poor. The trust level was 59.7 points out of a full mark of 100 points.
In 2010, the trust level was 62.9 points.
The study, conducted by the Institute of Sociology under the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, was based on a survey that asked more than 1,900 randomly selected residents in seven cities including Beijing and Shanghai about their opinions on trust.
The latest poll also found that in China, family members are viewed as the most trustworthy, followed by close friends and acquaintances.
It showed that around 30 per cent of the people polled trusted strangers on the street and about 24 per cent trusted strangers online.
When respondents were asked to name institutions that they generally trust, about 69 per cent said government, 64 per cent public media, 57.5 per cent non-governmental organisations, but only about 52 trusted commercial organisations.
The study also found that mistrust among different social groups, particularly between government officials and ordinary citizens as well as doctors and patients, has grown.
Wang Junxiu, who co-edited the blue book from the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, said the low level of trust in China has led to many problems such as the waste of resources.
To improve trust, Wang urged the government to work harder to ensure all powers are under close watch and punish people who operate scams.
– China Daily/ANN