Naomi Klein Excited About China’s Pledges Under China-US Climate Change Pact
Known for her firebrand critiques of capitalism in her previous works, Naomi Klein’s new book treads similar radical ground in the debate on climate change. In a recent National Geographic interview, Ms Klein shares her views on This Changes Everything. Of particular interest to this blog is her thoughts on the China-US climate change deal. While down on the US side of the bargain, she remains very enthusiastic about China’s commitments viz. renewable energy output. (However, this author is not persuaded by her position against shipping bitumen out of Alberta tar sands, either via the Keystone XL pipeline southward to the US or westward through the Northern Gateway pipeline proposal to the west coast and onward to Asian markets, specially China.)
There’s a new round of climate talks scheduled next year in Paris. How big a setback is the Republican victory in the midterm elections? Conversely, how important is the agreement on emissions between the U.S. and China that’s just been announced?
I think it remains to be seen how much the Republican victory is a setback. It also depends how important a climate legacy is to Obama. And whether the climate movement that came out with such enthusiasm in September can keep up the pressure on Obama. He has the power to say no to Keystone and protect the EPA from political meddling. It’s just a question of whether he wants to—especially in the face of Senator [James] Inhofe occupying one of the most important environmental positions in the country. It can’t be left to a battle between Obama and his conscience. It has to be about counterpressure from this growing movement.
As to the deal with China, the emissions that the U.S. commits to in the China deal are completely inadequate from the perspective of what climate scientists are telling us we need to do if we want to take the two-degree target seriously. We need to be cutting emissions by 8 to 10 percent per year. What this deal promises is 2.8 percent per year by 2025. And that’s not good enough.
The part of the China deal I’m most excited about is to have 20 percent of their energy mix coming from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030 and potentially earlier. We’re already seeing huge investment in clean energy in the PRC. Now they’re talking about doubling their share.
The entire interview can be seen at: http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/11/141126-keystone-pipeline-indigenous-canada-climate-change-ngbooktalk/
China Drafting New Law to Sanction Deployment of Troops Abroad
Given China’s long-standing principle/policy of not interfering in the domestic politics of other countries, if this law is adopted, it will signal China’s proactivism to take the fight against terrorists to the countries where they are training for anti-China attacks. As China matures as a dominant economic power with vital interests around the world and terrorism increasingly encroaches on Chinese turf, the law may also portend the first baby steps toward the revision of the country’s non-interventionist principle.
The draft of China’s first counter-terrorism law includes clauses that would authorize the army and the paramilitary police to carry out counter-terrorism missions abroad if the deployment had the consent of the countries involved, Chinese delegates told the Xiangshan Forum last week, according to analysts at the regional security meeting.
The draft legislation was submitted to the National People’s Congress Standing Committee in October and is not yet approved, the Hong Kong based South China Morning Post reported yesterday.
Li Wei, a counter-terrorism analyst at the China Institutes of Contemporary International Relations, said the legislation would authorize Chinese troops to fight terrorism beyond its borders.
The new law is being contemplated amid stepped up militant attacks carried out by the East Turkistan Islamic Movement, (ETIM) stated to be a Al Qaeda backed outfit in Xinjiang. A number of ETIM militants were reported to have been killed during air raids carried by Pakistan military in the tribal areas in recent months. Pakistan Prime Minister, Nawaz Sharif during his visit this month promised to step up the crackdown on the militant group. Xinjiang borders Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Li said Chinese troops rarely ventured abroad, with the most recent instance being in 2004 when armed police were sent
to guard the embassy in Iraq.
Renmin University international relations professor Jin Canrong said China was cautious about taking part in overseas operations, given its long-standing principle of non-interference in the internal affairs of other countries. But it was now prepared to be more proactive.
“It’s faced with escalating domestic terrorism threats, which have been proven to be connected to training and other terror activities abroad. Neighbouring countries are also calling on China to help in areas such as training counter-terrorism units and fighting Islamic State,” he said.
– The Economic Times (of India)
China Can Beat Its 2030 Pledge on Renewable Energy Output: IRENA
Under the China-US climate change agreement signed a couple weeks ago, China has pledged to cap emissions and up the amount of energy output from renewables to 20% from the current 8%. However, a recent report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) claims differently that China will only be able to raise renewables to 17% under a ‘current policies in place’ (business as usual) scenario. (It should be pointed out that IRENA overstates China’s current renewables capacities, stating the country had already attained 13% as of 2010.) There is already a loud chorus of nay-sayers and right-wing critics claiming China has pulled one over the US and/or the country won’t fulfill its commitments.
If we take IRENA’s report at face value, it means China will have to up its game even more to meet and even surpass its pledge. The report argues if China makes US$145 billion in renewables investment annually, up US$54 billion from current levels of investment, China would realistically be able to substantially increase energy output through renewables to 26% or 6% higher than its pledge. That indeed would be a great achievement but it remains to be seen whether China can afford that price tag. At the very least, however, as per an earlier post citing a University of Sydney China expert, once China makes a formal pledge, it sticks to it.
The report lays out a road map for China to meet its recently-announced target of capping emissions by 2030. China can double its renewable energy output to 26% by 2030 but only with an annual investment of $145bn.
“As the largest energy consumer in the world, China must play a pivotal role in the global transition to a sustainable energy future,” said Mr. Adnan Z. Amin, Director-General of Irena.
“China’s energy use is expected to increase 60% by 2030. How China meets that need will determine whether or not the world can curb climate change.”
Beyond business-as-usual
However, with current policies in place, the share of renewables in China’s energy mix will only rise to 17% by 2030. Irena suggest an annual investment of $145bn is needed – a $54bn boost beyond business-as-usual.
The higher renewable share will result in an annual saving of up to $228bn by 2030 when accounting for factors like human health and reduced emissions.
“China can continue its leadership in renewable energy by accelerating action in this area,” said Mr. Amin. “If China acts now to implement more renewable energy, it can reduce air pollution, enhance energy security, benefit its economy, and play a leading role in fighting climate change.”
China installed more renewable energy capacity in 2013 than Europe and the remaining Asia Pacific region combined. It is also a major exporter of renewable energy technology, accounts for two-thirds of global solar panel production, 90% of installed biogas systems, 40% of newly installed wind capacity in 2013, and provides 2.6 million jobs in its renewable energy sector.
– idie.net
The IRENA report can be downloaded from www.irena.org
Protesting Hong Kong Youths Worried About Their Economic Future
At the outset of the Hong Kong Occupy Central student protests in late September, this author had posted that behind the façade of demands for no holds barred electoral reform in 2017 was a deep-seated fear among Hong Kong youths (and some older cohorts) that Hong Kong’s advantages vis a vis major mainland cities are quickly being eroded. Hence, their desire to elect Hong Kong leaders that will ‘fight’ for their ‘rights’ to preserve those advantages. This CNBC video interview of a diehard protestor basically reflects those concerns.
But, the problem is Hong Kongers cannot have their cake and eat it too!.
Hong Kongers have to take the lumps along with the many benefits ‘one country, two systems’ has brought to the SAR. (That Hong Kong has enjoyed and is enjoying numerous benefits from the relationship was readily admitted by the interviewee.) When Hong Kong was far more advanced and affluent than their mainland counterparts, no complaints could be heard. It is only after the rapid growth of the mainland over the past few years, particularly following the Great Recession, that the contempt for mainlanders and the feeling that Hong Kongers were increasingly powerless to reverse the process has set in.
Frankly, the hope among protestors that Hong Kongers will elect a Chief Executive who will be able to effectively confront Beijing and ignite Hong Kong to revive its past glories is illusionary. With the further opening up of the mainland and deepening of reforms such as Shanghai’s free trade zone as well as others being contemplated – the Pearl River Delta greater area and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei integrated area, just to name a couple – the advantages that Hong Kong has enjoyed are slowly slipping away. It is no longer ludicrous to suggest that within another couple of decades, Hong Kong will simply become another Chinese city, the very fear of the protestors. Sadly but realistically, it’s an inevitability that many prominent economists and politicians have already alluded to.
So, go home protestors and try to better Hong Kong’s prospects through other more effective means before you lose them all.
The video can be seen at: http://video.cnbc.com/gallery/?video=3000332912
China Will Stick by Its Commitment on Climate Change: Expert
There are vocal China skeptics and critics out there that believe: 1) under the recent China-US climate change agreement, China gets away with “doing nothing”; and 2) even if China revs up counter-greenhouse gas policies, it won’t be able meet its commitment.
An earlier post cited a Tsinghua-MIT study that argued not only will China be able to meet its CO2 emissions commitments, it could reach peak emissions years before the target year of 2030 as specified under the agreement. Below is an analysis by Kerry Brown, Executive Director of the China Studies Center at the University of Sydney, on China’s decision making process that assures its commitment will stick.
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/kerry-brown/china-climate-change-deal_b_6159234.html?utm_hp_ref=world
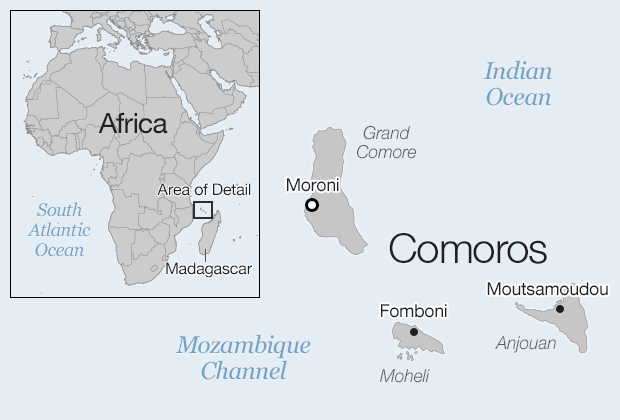
Chinese Company Wipes Out Malaria in Comoros in One Go
In the backdrop of China’s significant contributions to fighting the Ebola outbreak in West Africa (and yet be on the receiving end of unfair criticism from both uninformed Africans and Western media organizations, institutions, and governments), here is a prime example of Chinese companies trying to some good in Africa but getting panned for it.
On the tiny and desperately poor island country of Comoros sandwiched between the Southeast Africa coast and Madagascar, the scourge of malaria plagues the entire population. In partnership with the Comoran government, Chinese pharmaceutical company Artepharm has given doses of its malaria-fighting drug Artequick to over 700,000 people in a bid to wipe out the deadly disease on the islands completely. The drug has not been approved by international health organizations and the company is touting its success in Comoros to market to the rest of Africa.
This one-off mass administration campaign has virtually wiped out malaria there but because side effects have affected a very small segment of recipients, some Comorans are now complaining why the Chinese hadn’t given food and other aid instead. The WHO also got into the fray accusing Artepharm workers of insensitivity in their investigations of side effects as well as suggesting that a malaria-free Comoros could rob the people of their built-up immunity to malaria thereby creating conditions for an epidemic if the disease ever found its way back to the islands.
Well, you can’t have the cake and eat it too!
If the drug saves the country over US$11 million in medical treatment costs and contributes to stability in the country, the mass drug administration should be considered to have done a public good for the Comoros. The WHO is undoubtedly busy with its public health concerns around the world but there may be an element of sour grapes involved, having not thought of the seemingly incredible idea of eliminating the disease in one fell swoop. Having said this, the company probably should have done a better PR and treatment job in their handling of side effect issues.
Another issue has to do with market competition between Chinese pharmaceutical companies, the new kids on the block, and entrenched Western giants that don’t take kindly to Chinese corporate encroachments onto their traditional turf. Coartem, a rival to Artequick produced by Dutch company Novartis, is also vying for the African market and some bad publicity for Artepharm and its campaign on Comoros doesn’t do Novartis any harm.
Comoros Vice President Fouad Mhadji and Minister of Health dismissed criticism of the mass drug administration as propaganda fueled by Western rivals to the Chinese drug maker. “Why is Artequick bad? It is because it is sold by China,” Mr Mhadji told CBS.
The article and accompanying video report can be seen at: http://www.cbsnews.com/news/chinas-test-malaria-drug-artequick-experiment-on-population-of-comoros/
Most Hong Kongers Want Protesting Students to Go Home: Poll
Although the Chinese University of Hong Kong survey of community sentiment toward the Occupy Central protests has been mentioned in the press, it is worthy to take a more detailed look at its results. Just after the poll’s release last Sunday, the police moved in to dismantle the barricades at the main protest site in Admiralty as a group of radicalized students tried to break into the Legislative Council building resulting in several arrests.
A third round of telephone interviews was conducted in local Cantonese dialect of 1030 Hong Kong citizens 15 years and older by the university’s Center for Communication and Public Opinion Survey between November 5-11, the results (with a response ratio of 42% and margin of error of 3.1%) of which were released on November 16. The results showed Hong Kong citizens clearly feed up with the students’ rancor and demanding a swift end to the blocking of streets.
Asked whether they supported the Occupy Central protests, 43.5% replied in the negative (extremely do not support or relatively do not support), nearly as many as in September (46.3%) when the protests began but up substantially from October (35.5%) Those who vigorously or somewhat supported the protests declined to 33.9% from 37.8% in October. The survey also discovered the younger the age cohort, the greater the propensity to support for the protests with over 2/3 (67.7%) of the 15-24 year old grouping strongly or relatively supporting the movement. Moreover, the poll found the higher the education, the more the support.
On the question of whether the students should retreat from the protest sites immediately, an overwhelming majority (67.4%) said they should or really should with only 13.9% saying they should hunker down. As with their attitudes toward Occupy Central, the older the cohort, the greater the demand for abandonment. Notably, 59.7% of the 25-39 year group wanted the students to leave and 53.9% of college or higher educated indicated the same. Also, interestingly, 73.3% of centrists (neither China, business, nor pan-democrat leaning) and 80.4% of those without any political affiliation wanted the students to get out. Even 39.9% of radical and moderate democrats agreed the students should dump their campaign.
As to whether they trusted the police to do the right thing, most respondents (55.6%) said in the affirmative, up 11.5% over October. Those distrusting the police fell from 28.6% in October to 20% this time round. The police was graded 6.25 out of 10 for their handling of the students, up from 5.49 in October. Asked whether they were confident about Hong Kong’s future, while pessimists (34%) outnumbered optimists (25.3%), the percentage of pessimists has steadily declined since September (45.6%) and October (37.7%) with optimism going up since September (21.2%). Yet, sentiment about Hong Kong was graded at 4.8/10 above the range for pessimism (0-4) and up from September (4.22) and October (4.57).
However, another poll conducted on November 11-12 Of 510 Hong Kong residents by American firm Selzer & Co. for Bloomberg Global Poll with a margin of error of 4.3% found 87% of respondents saying the protests did not divert financial activity away from the city, a fear that was greatly exaggerated by the foreign press who suggested global investors would flee Hong Kong for safer havens like Singapore. Nonetheless, 57% still felt business would be driven away if the students stayed on while less than 1/3 (30%) believed the protests were unlikely to exert a palpable affect on the city’s position as a financial center.
But, returning to the Chinese University of Hong Kong survey, ominously for the 2017 election of the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong SAR, 46.7% responded that the Legislative Council should not approve of any vetos on candidates made by the central government. Although down from 53.7% in September (48.5% in October), it is still 10.6 percentage points higher than those wanting the Legco to vote in favour (36.1%) who have increased from 29.3% in September. On the other hand, if the central government eliminates company and executive votes in the Election Council, leaving it entirely to individual voting by the ‘four big communities’ in Hong Kong society to elect members, then 45.4% would approve as compared to 35% opposed.
So, there is still room for compromise and Hong Kong may again draw the eyes of the world during the run-up to 2017.
Chinese Aid Abused by African Leaders: Report
Notwithstanding China’s long-standing policy of non-interference in the domestic politics of other nations, if this report is accurate that African leaders are indeed heavily engaging in patronage politics and funneling large amounts of largesse to their home states, perhaps the Chinese government should consider some minor ‘conditions’ on official aid. Not the strict ‘conditionalities’ that come with World Bank and Western country aid but the simple requirement that independent commissions be set up in host nations to determine where the aid should go. Perhaps that would help curb some of the abuses.
China’s “no strings attached” aid is being abused by African leaders who channel the lion’s share of funds to their home areas, U.S.-led researchers found in the first geo-referenced database of Chinese aid to the world’s poorest continent.
China is a favoured donor for many African presidents, weary of the conditions attached to Western aid, ranging from combating corruption to respecting gay rights.
In contrast, China’s policy of non-interference means it rarely intervenes in domestic issues. This makes it easy for corrupt politicians to use Chinese aid to reward their political supporters, rather than direct it to the areas most in need, researchers said.
“Our research found that the home regions of African presidents receive three to four times more Chinese aid,” Roland Hodler, a professor of economics at Switzerland’s University of St Gallen, said in a statement.
“This suggests that the Chinese principle of non-interference in domestic affairs allows African presidents to use Chinese aid for patronage politics.”
Researchers from German, Australian, Swiss and U.S. universities mapped more than 1,600 Chinese official development aid projects, worth $84 billion, in 50 African countries between 2000 and 2012.
Their paper highlights a “fancy new” Chinese-built school in the remote village of Yoni, hometown of Sierra Leone President Ernest Koroma, and the role of Chinese railway and dam projects in helping President Joseph Kabila of the Democratic Republic of Congo win re-election in 2011.
Ghana, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Ethiopia were the largest recipients of Chinese aid in Africa, which receives more than half of the superpower’s global assistance.
The researchers argue that projects funded for political reasons are less likely to contribute to development than those allocated on the basis of poverty or need.
“We hope that this effort will… facilitate evidence-based discussion and debate among those who want to see foreign aid put to more effective use,” Brad Parks, co-executive director of the AidData research lab at the College of William and Mary in the United States, said in a statement.
– Reuters
China’s CO2 Peak Could be Reached Much Sooner
An earlier post on the recently signed China-US climate change agreement cited a 2011 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory study that predicted China’s CO2 emissions would peak in 2030 which coincided with China’s pledge. However, MIT-Tsinghua researchers suggest the peak period could be moved forward by as many as 5 years given China’s slowing economy and the country’s many pollution-fighting policies. I would add the transition to domestic consumption, the requisite changes in industrial structure, reducing heavy polluting industries such as iron and steel and cement, as well as moving up the economic and financial ladder generally also contribute to reductions in CO2. Changes in life-styles and attitudes, especially among the next generation of consumers, make it all the more conducive.
As recently as 2010, when China’s economy was still growing at more than 10 percent a year, it was unclear when its emissions might peak, says Valerie Karplus, a professor of global economics at MIT’s Sloan School of Management, and director of the Tsinghua-MIT China Energy and Climate Project.
But economic growth has slowed (it was 7.7 percent in 2012), and in turn so has growth in demand for energy. Also, this year China’s government has already announced a plan to reduce air pollution by taxing and limiting coal use. Beyond that, carbon trading systems are now being tested in five cities and two provinces, and a national system is expected to come online in 2016.
But, says Karplus, there is still uncertainty over when China will begin actually reduce its emissions, and by how much. “It makes a big difference whether it peaks at 10 billion, 11 billion, or 15 billion metric tons of CO2,” and whether or not the trajectory decreases rapidly after that peak, says Karplus. The (China-US climate change) pact is “hugely important” for global climate change policy efforts because China has finally agreed to a target related to “turning its emissions down in absolute value,” instead of just limiting the rate at which those emissions grow from year to year, says Michael Oppenheimer, a professor of geosciences and international affairs at Princeton University. The deal also has symbolic value, he says, since the world’s top two emitters have effectively circumvented the reigning geopolitical gridlock over international climate policy.
– MIT Technology Review
Arch Sinophobe Jimmy Lai Wants Student Protestors to Retreat
Jimmy Lai, the rabidly anti-CPC, anti-mainland media tycoon who had financially and otherwise supported Occupy Central and the protesting students from the outset, including protest training tutored by foreign anti-China groups, now wants the students to retreat and regroup for fear of further antagonizing the vast majority of Hong Kong citizens.
Meanwhile, after the police began dismantling student barricades on court order, yesterday evening, a group of radical students broke the glass facade of the government’s legislative council building using barricades in an attempt to storm into the building as other protesters blocked police from interfering.
Unrelenting China critic Lai has been a regular at one of Hong Kong’s key Occupy protest sites: in Admiralty almost every day, returning nightly to his family in upscale Kowloon Tong. He remains despite having been attacked last week – by three men hurling bags of rotten offal – and regardless of a threatened clearance of the area by bailiffs and police. Vowing to continue his sit-in while the protest continues, he says that if officers turn up: “I will let them arrest me. I will not resist.”
Ironically, while Lai, 65, bolsters the pro-democracy camp, he also believes that, strategically, the protesters should now retreat. This as a small group of people early this morning tried to break into Hong Kong’s Legislative Council nearby, causing riot police to deploy pepper spray to prevent others from following suit.
“People are getting tired…We cannot exhaust the goodwill of the people,” says Lai, on the day that results of a Chinese University poll showed almost 70 per cent of Hong Kong people, sick of traffic jams and lost business, want the Occupiers to leave. “But it doesn’t mean we have to yield.”
Lai reckons the students and their fellow dissenters should withdraw and re-energize – and vow to return if their demands remain unheeded. “We should retreat when the momentum is there, while our determination and will are strong,” he says. “Then we will be able to come back.”
Despite Lai’s support for the students, he also believes their recent attempt to meet Chinese authorities in Beijing was a mis-step. “For them to do it [on Saturday] was not appropriate,” he says. “They should have gone during APEC, when world leaders were there. That would have created the biggest impact.”
The attempt by three Hong Kong Federation of Students representatives to fly to the Chinese capital was foiled by the invalidation of their travel documents. Entry permits, issued by mainland authorities, allow Hong Kong residents free travel over the border.
He acknowledges that those who have dug in their heels at the Occupy sites constitute a minority of Hong Kong’s 7.2 million population. “Only a small percentage of people are willing to pay the price to fight,” he says.
– Sydney Morning Herald